Introduction
The global healthcare sector has been witnessing a tremendous surge in demand for antiviral therapies, particularly those aimed at treating liver infections. The hepatic antiviral drugs market, therefore, plays a pivotal role in this evolving landscape. Chronic liver diseases, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C, affect millions of individuals worldwide, leading to severe complications such as liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver failure. As a result, the necessity for effective antiviral interventions has never been more crucial.
Moreover, the rise in awareness, diagnosis rates, and treatment-seeking behavior among patients has accelerated the development and distribution of hepatic antiviral drugs. Governments, healthcare institutions, and pharmaceutical companies are increasingly collaborating to bring novel therapies to market. Thus, the hepatic antiviral drugs market has emerged as a dynamic segment within the broader pharmaceutical industry, with significant implications for global public health.
Source: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-hepatic-antiviral-drugs-market
The Evolution
Initially, treatment options for hepatic viral infections were limited, often associated with adverse effects and low success rates. Interferon-based therapies were among the earliest interventions, offering modest efficacy but often accompanied by considerable toxicity. This led to widespread treatment hesitancy and poor adherence.
However, the landscape began to change dramatically with the advent of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs), particularly for hepatitis C. These drugs offered cure rates exceeding 95%, shorter treatment durations, and significantly fewer side effects. Likewise, for hepatitis B, nucleoside/nucleotide analogues revolutionized disease management by effectively suppressing viral replication.
Over the years, ongoing research and innovation have continued to refine these therapies. New drug combinations, extended-release formulations, and personalized medicine approaches have further enhanced treatment outcomes. In parallel, improvements in diagnostic tools and screening programs have facilitated early detection, enabling timely therapeutic interventions.
Market Trends
Several noteworthy trends are shaping the hepatic antiviral drugs market. First and foremost, there is a marked shift toward combination therapies that offer synergistic benefits. These combinations not only increase efficacy but also reduce the risk of resistance development, a critical concern in antiviral treatment.
Additionally, the market is experiencing a surge in demand for oral medications, which are more convenient and improve patient adherence. The development of pan-genotypic drugs for hepatitis C, which are effective across all viral genotypes, has simplified treatment protocols and broadened access.
Another significant trend is the growing focus on drug affordability and accessibility. Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly adopting tiered pricing strategies, especially in low- and middle-income countries. Moreover, the rise of generic manufacturing is helping to bring down costs and expand reach.
Furthermore, the integration of digital health solutions is transforming patient management. Telemedicine platforms, digital adherence tools, and real-time monitoring systems are enhancing treatment compliance and patient engagement. These technological advancements are proving particularly valuable in regions with limited healthcare infrastructure.
Finally, robust research pipelines and strategic partnerships are driving innovation in the field. Numerous clinical trials are underway to develop novel molecules, improve existing formulations, and explore new indications. Consequently, the market continues to evolve in response to changing epidemiological patterns and treatment needs.
Challenges
Despite its promising trajectory, the hepatic antiviral drugs market is not without challenges. A primary concern is the persistent stigma associated with hepatitis infections, particularly in conservative societies. This often leads to underreporting, delayed diagnosis, and suboptimal treatment uptake.
Moreover, drug resistance remains a significant threat, especially with long-term monotherapy use. While combination therapies mitigate this risk, they also raise concerns about increased treatment costs and potential side effects.
Access to care is another critical issue, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Limited availability of diagnostic services, coupled with high drug costs, restricts treatment coverage. This is further compounded by healthcare workforce shortages and inadequate infrastructure.
Additionally, regulatory hurdles and lengthy approval processes can delay the introduction of new therapies. Variability in clinical guidelines across regions also creates inconsistencies in treatment approaches, potentially impacting patient outcomes.
Furthermore, funding constraints and shifting healthcare priorities, especially in the post-pandemic era, pose financial challenges for public health programs targeting viral hepatitis elimination.
Market Scope
The scope of the hepatic antiviral drugs market is extensive, encompassing a wide range of drug classes, therapeutic indications, and end-user segments. The market includes interferons, nucleoside/nucleotide analogues, direct-acting antivirals, and emerging biological therapies. Each category addresses specific viral strains and stages of liver disease progression.
In terms of indications, the market primarily focuses on hepatitis B and hepatitis C, though research is expanding into other viral hepatitis forms such as hepatitis D and E. Moreover, co-infections with HIV and other comorbidities are increasingly influencing treatment decisions and market dynamics.
The end-user landscape includes hospitals, specialty clinics, ambulatory care centers, and community health programs. Pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and government agencies also play integral roles in shaping the market.
Geographically, the market spans high-income nations with advanced healthcare systems, as well as low- and middle-income countries grappling with high disease burdens. This global distribution underscores the need for diversified strategies and localized solutions.
Furthermore, the scope extends beyond drug therapy to include diagnostic testing, patient education, post-treatment monitoring, and preventive interventions. As such, the hepatic antiviral drugs market represents a holistic approach to liver health management.
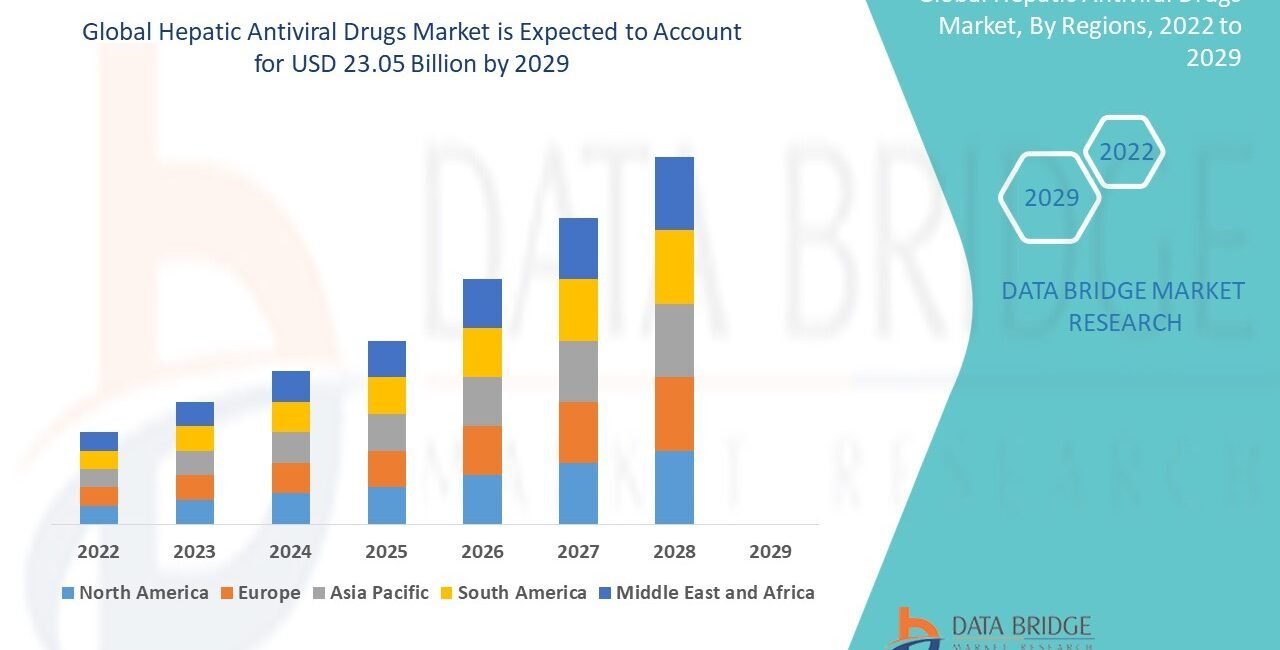
Market Size
The hepatic antiviral drugs market has demonstrated strong and sustained growth over the past decade. Driven by rising disease prevalence, improved diagnostics, and expanding treatment access, the market has witnessed substantial investments and revenue generation.
In recent years, the approval of highly effective DAAs and the scale-up of hepatitis elimination programs have contributed significantly to market expansion. Global initiatives aimed at diagnosing and treating millions of individuals have stimulated pharmaceutical sales and bolstered manufacturing capacities.
The market size is expected to continue its upward trajectory, fueled by several key factors. These include aging populations, increased screening efforts, and ongoing drug development. Additionally, the growing prevalence of liver disease linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity and alcohol consumption is likely to sustain demand.
Regionally, North America and Europe currently dominate the market, owing to high treatment rates and well-established healthcare infrastructures. However, Asia-Pacific and Africa are emerging as high-growth regions due to escalating disease burdens and policy-driven healthcare improvements.
Overall, the market’s financial outlook remains robust, with analysts projecting consistent compound annual growth rates (CAGR) and expanding profit margins for key players.
Factors Driving Growth
Several interrelated factors are propelling the growth of the hepatic antiviral drugs market.
First and foremost, the global rise in hepatitis B and C cases has created an urgent need for effective treatments. These infections, if left untreated, can lead to severe liver damage and mortality, thereby driving demand for antiviral therapies.
Secondly, advances in drug development have significantly improved treatment outcomes. The availability of highly effective DAAs and long-acting formulations has made therapy more accessible and acceptable to patients.
Thirdly, increased governmental and non-governmental support has enhanced funding for hepatitis programs. National strategies aimed at disease elimination are promoting widespread testing and treatment coverage.
Fourthly, growing awareness campaigns and advocacy efforts are breaking down social stigma, encouraging more individuals to seek diagnosis and care. Public education initiatives, supported by civil society organizations, are playing a vital role in this transformation.
Fifthly, the expansion of healthcare infrastructure, especially in emerging economies, is facilitating better access to antiviral drugs. New clinics, telemedicine platforms, and mobile health units are reaching previously underserved populations.
Sixthly, strategic alliances between pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and public health agencies are accelerating innovation and market penetration. These collaborations are enabling faster drug approvals, more efficient supply chains, and targeted outreach programs.
Lastly, the increasing integration of digital technologies is enhancing treatment adherence, monitoring, and patient engagement. From AI-driven diagnostics to smart medication reminders, these tools are optimizing the therapeutic experience and driving better outcomes.

