The Rise of Laparoscopic GI Surgery
In recent decades, Laparoscopic GI Surgery has revolutionized the way gastrointestinal (GI) disorders are treated. This minimally invasive technique uses small incisions and specialized instruments, significantly improving recovery times, reducing postoperative pain, and enhancing surgical precision. As awareness grows, more patients and specialists are choosing laparoscopic methods over traditional open surgeries, especially for gastrointestinal conditions like appendicitis, hernias, gallbladder stones, and even colorectal cancers.
For those dealing with persistent digestive issues, early consultation and understanding of available surgical options like laparoscopy can lead to better health outcomes.
What Is Laparoscopic GI Surgery?
Laparoscopic GI Surgery, also known as minimally invasive gastrointestinal surgery, is a surgical technique where operations in the abdominal area are performed through small incisions—usually no more than 1-2 cm each. A laparoscope (a tiny camera) and other instruments are inserted through these ports to perform the necessary procedure. The camera sends real-time images to a monitor, allowing the surgeon to see inside the body with precision.
This technique is widely used for surgeries such as:
- Gallbladder removal (Cholecystectomy)
- Appendectomy
- Hernia repairs
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) treatments
- Colectomy for colon diseases
- Obesity and metabolic surgeries
Key Benefits of Laparoscopic GI Surgery
Choosing laparoscopic procedures over open surgery offers numerous advantages:
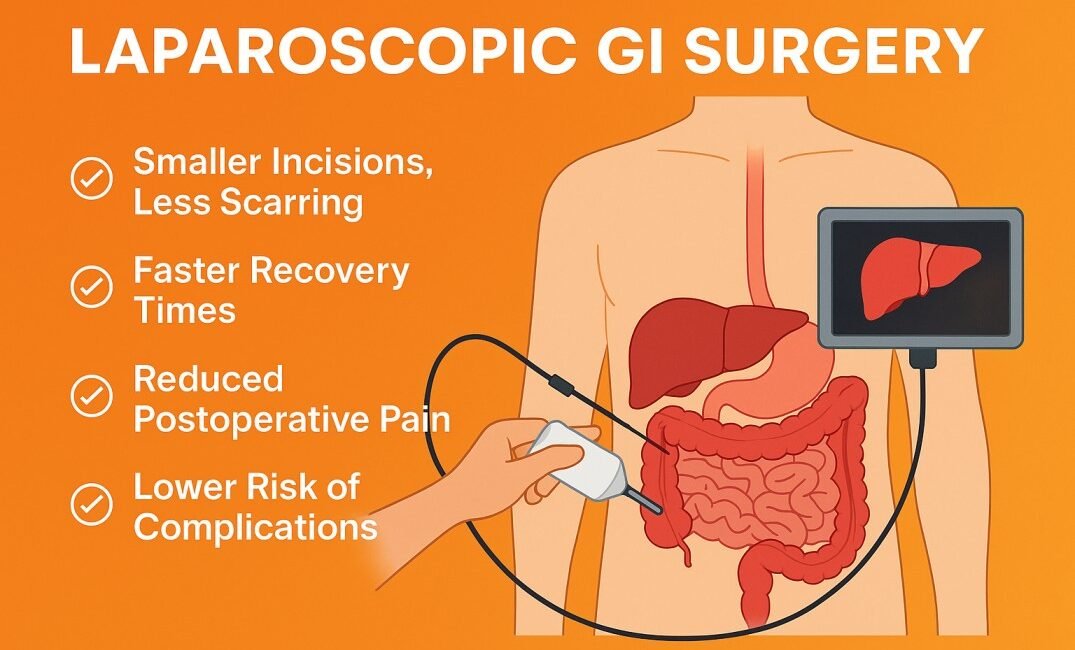
1. Smaller Incisions, Less Scarring
One of the most apparent benefits is the reduced size and number of incisions, which not only minimizes visible scarring but also reduces the risk of infection.
2. Faster Recovery Times
Most patients undergoing laparoscopic GI surgery can return to normal activity within a few days to a week, compared to weeks or months with open surgery.
3. Reduced Postoperative Pain
With fewer and smaller incisions, patients experience significantly less postoperative discomfort, often requiring minimal pain relief medication.
4. Lower Risk of Complications
Minimally invasive surgery means less trauma to the body, reducing risks like bleeding, infection, or wound dehiscence (incision reopening).
5. Shorter Hospital Stays
Many laparoscopic procedures can be performed as day-care surgeries, with patients going home the same or the next day lowering hospital bills and infection risks.
Common GI Conditions Treated with Laparoscopy
Here are a few gastrointestinal disorders commonly treated using laparoscopic techniques:
Gallstones and Cholecystitis
Gallbladder removal is one of the most frequently performed laparoscopic surgeries. It helps relieve pain, digestive disturbances, and the risk of infection due to gallstones.
Appendicitis
A laparoscopic appendectomy is now the gold standard for treating acute appendicitis, offering a much faster return to daily activities.
Hernias
Inguinal, umbilical, and hiatal hernias can be repaired effectively using mesh via laparoscopy, leading to quicker healing and reduced recurrence rates.
Acid Reflux and GERD
Laparoscopic fundoplication is performed to treat chronic acid reflux, helping patients who don’t respond well to medication.
Colon and Rectal Conditions
From inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) to colorectal cancer, laparoscopy can aid in diagnosis, biopsy, and partial or total colon removal with improved outcomes.
Recovery and Aftercare: What Patients Should Know
Post-surgery recovery is smoother with laparoscopic GI surgery, but proper aftercare remains crucial for optimal outcomes.
🔹 Immediate Post-Op
- Most patients can start drinking liquids within hours after surgery.
- Discharge is usually possible within 24-48 hours.
🔹 At Home
- Light activities can be resumed in a few days.
- Full recovery typically occurs within 1-2 weeks.
- Follow dietary instructions provided by the surgeon or dietitian.
🔹 Follow-Up
- Stitches or surgical glue incisions may not require removal.
- Regular follow-up visits ensure healing and rule out complications.
When Is Laparoscopic GI Surgery Not Recommended?
While highly effective, laparoscopy may not be suitable for every patient or condition. Cases where open surgery might be preferred include:
- Extensive internal adhesions due to previous surgeries
- Large tumors or significant inflammation
- Emergency conditions with severe infection
- Patients with underlying heart or lung disease that limits tolerance to general anesthesia
A thorough evaluation, including imaging and medical history review, will help determine the right approach.
Why Expertise Matters in Laparoscopic GI Surgery
The success of laparoscopic procedures is closely tied to the skill and experience of the surgical team. Precision, advanced tools, and proper preoperative planning are essential to avoiding complications and achieving the best results.
LGI Hospitals, known for their gastroenterology and surgical departments, offer advanced laparoscopic interventions using the latest technology. Their team of GI surgeons, anesthetists, and post-op care staff ensure personalized treatment tailored to each patient’s needs.
Final Thoughts: Embracing Modern GI Care
Laparoscopic GI Surgery has emerged as a game-changer in the field of gastrointestinal medicine. Whether it’s a routine gallbladder removal or a complex colon surgery, the benefits of minimal invasiveness, quicker recovery, and improved outcomes cannot be overstated.
With experienced specialists and modern infrastructure, institutions like LGI Hospitals are paving the way for safe, efficient, and patient-centered laparoscopic care. If you or a loved one is exploring options for GI issues, it’s worth considering laparoscopic treatment and getting expert medical advice early on.

